Ever tried the Burma Bridge? One wrong foot on the block, and your whole body is in the air. Craving to get on the surface as soon as possible.
Frankly, balancing SEO is just like that. One wrong decision can make you witness rock-bottom to your website traffic to desired CRM tool. This wrong move can lead your site to page 10 or worse.
Your SEO approach should integrate well to help visitors discover your site effectively through SERPs and navigate your content before building customer loyalty.
Companies that neglect either part of this equation face missed chances because excessive SEO optimization harms user relationships or bad SEO visibility causes sites to disappear from search results.
There is a fine line between what your audience craves and what search engines like. It requires experience to see that fine line and hit the SEO nail on the head.
This is where ThriveCraft SEO enters. We have a legacy of over ten years. We do not just dive right in. We first identify your SEO goals, identify the perfect one for your growth, and implement your specific SEO strategy backed by our expertise to generate results that last longer. You can book a free call with us to get started.
What Do You Mean by SEO Balance?
Search Engine Optimization balance exists when website optimization meets search engine requirements together with excellent user experiences. It balances different SEO elements to get maximum visibility and organic traffic and to make content valuable and interesting to users.
Why Balancing SEO Elements Matters?
The balance of SEO elements. Here are five reasons why they matter so much:
Improved Search Visibility:
SEO improves the position of your website content because it enables better search engine ranking, which enhances user discoverability. Search engine optimization through keyword stuffing will lead to reductions in search engine rankings and penalties.
Enhanced User Experience (UX):
Your website stays engaging to customers when UX functions well since it allows them to discover additional pages. Visitors will leave your website due to poor UX even though it maintains a good search engine ranking.
Sustainable Growth:
Every organization benefits from creating a solid framework that integrates technical SEO with content production alongside UX optimization for sustainable expansion. When any component of SEO remains untreated, it produces unusable results, including attractive content without audience reach and enhanced web pages that do not trigger engagement.
Alignment with Search Engine Algorithms:
Current search engines base their results on user engagement signals that measure how long users stay on pages and their tendency to navigate away. Organizations that maintain an equilibrium between SEO practices and user needs will achieve compliance with current standards.
Increased Conversions:
The combination of maximal site optimization with user-friendly interfaces leads to customer conversions, which generate additional revenue while strengthening brand loyalty.
The Process of Balancing Content and Keywords
How to Balance Keyword Placement and Readability
Optimal Keyword Density: Use a keyword density of 1-2% (about one keyword per 100-150 words) without repetitive use to stay visible.
Strategic Placement: Position primary keywords in important locations like title, meta description, headings, and the first 200 words of content. Use secondary keywords naturally in the text.
Prioritize Readability: Position sentences so that they come naturally around keywords. When a keyword sounds unnatural or causes confusion, reword or eliminate it.
Leverage Synonyms and LSI Keywords: Utilize synonyms (Latent Semantic Indexing or LSI keywords) in place of repetition to ensure relevance.
Optimize Keyword Strategy: Quality vs. Quantity
Quality over Quantity: Avoid bombarding your content with several terms by using fewer, closely related keywords. This enhances targeting and prevents watering down the message.
Long-Tail Keywords: These specific phrases tend to have less competition but greater conversion potential, making them a great addition to your plan.
Semantic Search Optimization: Optimize context through the use of keyword variations to meet the way search engines perceive intent instead of exact matches.
Match Keywords with Search Intent
Understand Intent Types:
Informational: Users search for knowledge (e.g., “how-to guides”).
Navigational: Users search for exact sites or brands.
Transactional: Users are going to buy or do something.
Content Alignment: Produce content specific to each intent type (e.g., blog articles for information searches, product pages for transactional searches.)
Use Topic Clusters: Cluster associated keywords by themes that are indicative of user need, enhancing content relevance and SEO performance.
Content Creation: SEO vs. User Experience
How to Create Content for Search Engines and Users
Understand User Intent:
Look at what users are searching for when they query certain keywords. Content must respond to their questions directly and offer solutions.
Examine top-ranking pages to see patterns of how they fulfill user requirements.
Optimize Content Without Sacrificing Readability:
Apply keywords judiciously in titles, headings, meta descriptions, and throughout the copy without overwhelming it.
Write naturally and conversationally to engage readers without sacrificing search engine optimization.
Prioritize Structure and Accessibility:
Employ clear headings, bullet points, and brief paragraphs for scannable content.
Make your site mobile-friendly and load it fast to improve SEO and UX.
Utilize Visuals and Interactive Elements:
Insert images, videos, infographics, or interactive tools to make content more interesting while enhancing
dwell time—a primary SEO indicator.
The Role of Engaging and Relevant Content
User Engagement:
Engaging content makes users spend more time on your site, indicating to search engines that your page is important.
Relevance:
Pertinent content that addresses user issues establishes credibility and authority and invites repeat visits and sharing.
Search Engine Rankings:
Search engines favor content that matches users’ intent and offers an uninterrupted experience.
Update Old Content vs. Creating New Content
When to Update Old Content:
Refresh outdated statistics or data.
Improve underperforming pages through enhanced keyword use or new content sections.
Upgrade formatting or graphics to align with present UX guidelines.
When to Create New Content:
Deal with new trends or subjects not mentioned in your current content.
Pursue new keywords or consider alternative formats such as videos or podcasts.
The best is to Combine Both Approaches:
Review your content library regularly to find gaps or opportunities to refresh while maintaining a constant stream of new material.
Technical SEO vs. User Experience
How to Optimize Site Speed for SEO and UX
Optimize Page Load Times:
Optimize images and videos to minimize file sizes while preserving quality.
Apply browser caching to save static files locally on users’ devices to load faster on repeat visits.
Take advantage of Core Web Vitals:
Prioritize metrics such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) to enhance page performance and reliability.
Activate Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
CDNs spread content over several servers worldwide, lowering latency and enhancing load times for users who are far away.
Optimize Code:
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files to eliminate unnecessary characters.
Prevent render-blocking scripts that slow down page rendering.
Balance Mobile Optimization with Desktop Performance
Mobile-First Design:
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, priority is placed on mobile-device design with desktop compatibility.
Utilize responsive web design to dynamically adapt layouts according to screen size.
Touch-Friendly Elements:
Make buttons, menus, and links accessible for simple clicking on smaller screens without unintended tap action.
Test Across Devices:
Test your site frequently on different devices with tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to flag problems.
Desktop Optimization:
While mobile-focused, don’t forget about desktop users. Make sure to provide quick load times, big pictures, and simple navigation for big screens.
Navigate Internal and External Linking Strategies
Internal Linking:
Link similar pages on your website to enhance navigation and share link equity (SEO value).
Apply descriptive anchor text containing keywords so search engines can comprehend the context of linking pages.
External Linking:
Link to relevant external sources so that users receive extra value.
Ensure links to external pages open in a new tab to keep users on your site longer.
Avoid Broken Links:
Periodically scan your site for dead links through tools such as Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to ensure a seamless user experience.
Balance Quantity with Quality:
Don’t add links excessively that can overwhelm users or dilute SEO value. Prioritize links that actually add relevance to the content.
On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO
How to Balance Meta Tags, Headings, and URLs for SEO
Meta Tags:
Compose short and keyword-dense title tags (less than 60 characters) that reflect the page content.
Design effective meta descriptions (less than 160 characters) to enhance click-throughs. Though not a direct ranking signal, they affect user behavior.
Headings:
Utilize hierarchical heading tags (H1 for primary title, H2-H6 for subheadings) to organize content logically.
Use primary keywords in headings, but make them natural to prevent keyword stuffing.
URLs:
Make URLs short, descriptive, and keyword-oriented (e.g., example.com/seo-tips).
Avoid special characters or unnecessary parameters; use hyphens to divide words.
The Role of Backlink Profile in SEO Performance
Quality backlinks from reputable sites indicate trustworthiness to search engines, which enhances rankings.
A diverse backlink profile (links from multiple domains) lessens reliance on any one source.e
Anchor Text Optimization: SEO vs. Natural Flow
SEO View:
Utilize descriptive anchor text with keyword-relevant text to enable search engines to comprehend the context of the linked page.
Do not over-optimize (e.g., too many exact-match keywords), which can lead to penalties.
Natural Flow View:
Ensure anchor text naturally occurs within the sentence or paragraph for improved readability.
Utilize a combination of branded terms (e.g., “Your Site”), generic phrases (e.g., “click here”), and keyword-rich anchors for balance.
Link Building: Quality vs. Quantity
How to Acquire High-Quality Backlinks
Create Link-Worthy Content:
Write in-depth guides, case studies, infographics, or original research that tends to attract links from high-authority sites.
Target solving specific problems or answering questions that are relevant to your niche.
Use Digital PR:
Work with journalists or bloggers to get your content published on high-authority sites.
Utilize tools like HARO (Help A Reporter Out) to connect with media professionals looking for expert opinions.
Guest Posting:
Create guest posts for authoritative sites within your niche, ensuring the content is useful and has a contextual backlink.
Broken Link Building:
Find broken links on high-authority pages and propose your content as an alternative.
Build Relationships:
Connect with influencers, bloggers, and industry influencers to get backlinks through partnerships or collaborations.
The Role of Guest Posting and Outreach
Guest Posting:
Guest posting continues to be an effective method to achieve high-value backlinks by posting quality content to reputable websites.
Target established websites with high domain authority and relevance within your niche to yield the maximum result.
Outreach:
One-on-one outreach efforts addressed directly to webmasters or website editors can attain backlinks.
Explain well-structured value while outreach as a means to let them understand how your article fits into and augments their content or appeals to their crowd.
Avoid Overuse:
Too much guest blogging on low-authority sites will be spammy and hurt your backlink profile. Focus more on quality rather than quantity with outreach efforts.
Balance Link Diversity and Authority
Link Diversity:
A natural backlink profile consists of links from different sources like blogs, news pages, forums, directories, and social media sites.
Don’t over-rely on a single source of links, as this may look unnatural to search engines.
Link Authority:
Give more importance to backlinks from high-authority sites (e.g., government websites, universities, or industry leaders).
A single authoritative backlink can be more valuable than dozens of low-quality links for SEO.
Track SEO Performance and Adjustments
How to Monitor SEO Metrics and KPIs
Key Metrics to Monitor:
Organic Traffic: Track the number of visitors from search engines through tools such as Google Analytics 4 (GA4) or Google Search Console (GSC.)
Keyword Rankings: Track keyword positions over time using tools such as Semrush, Ahrefs, or SE Ranking.
Core Web Vitals (CWV): Track page speed, interactivity, and visual stability through GSC or site audit tools.
Backlink Profile: Monitor lost and gained backlinks, referring domains, and link quality through tools such as Ahrefs or Semrush Backlink Analytics.
Click-Through Rate (CTR): Measure how frequently users click your site after they view it in search results with GSC.
Engagement Metrics: Watch for bounce rates, average session duration, and scroll depth to measure user interaction.
The Importance of A/B Testing in SEO
Test Changes Safely:
Experiment with meta tags, headlines, content formats, or internal linking structures on a segment of your audience before rolling out changes sitewide.
Measure Impact:
Compare performance metrics such as traffic, CTR, or conversion rates between the control group (unchanged content) and the test group.
Tools for A/B Testing:
Use platforms like Google Optimize or Optimizely to run controlled experiments.
Examples of A/B Tests in SEO:
Test different title tags to see which generates higher CTRs.
Experiment with content layouts for better engagement metrics.
Make Data-Driven SEO Adjustments
Analyze Performance Data:
Compare metrics such as keyword positions, organic traffic movements, and backlink development regularly.
Spot pages that underperform with tools like Ahrefs’ Site Explorer or GSC’s Performance Report.
Fine-tune according to Insights:
Enhance the relevance of content by using target keywords that show greater congruence with the user’s intent.
Solve technical glitches like nonfunctioning links or slow websites reflected in site audits.
Competitor Analysis:
Track competitors’ strategies through instruments like Semrush or Ahrefs to catch loopholes within your strategy.
Iterative Improvements
Always optimize what is working—enhancing content quality, gaining more authoritative links, or improving UX.
SEO Goals vs. Business Objectives
Align SEO Strategy with Business Growth
Start with Business Objectives:
Determine top-level goals like revenue growth, market share expansion, or new product launches.
Determine how SEO can assist directly in achieving these goals. For instance, if the goal is lead generation, the SEO strategy could emphasize ranking for high-intent keywords and landing page optimization for conversion.
Set SMART SEO Goals:
Apply the SMART framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to develop actionable SEO goals.
Example: “Grow organic traffic to product pages by 30% in six months.”
Integrate Keywords with Business Goals:
Coordinate keyword research with user intent and business objectives. For example, rank keywords focusing on potential buyers instead of driving traffic.
Collaborate Across Teams:
Facilitate coordination between SEO, marketing, sales, and product teams to develop a cohesive keyword strategy that drives business growth.
Measure SEO Success Beyond Rankings
Track Business-Oriented KPIs:
Organic traffic on high-value pages.
Conversion rates from organic search traffic.
Revenue or leads driven by SEO efforts.
Focus on Engagement Metrics:
Track bounce rate, time spent on a page, and scroll depth to gauge how well your content connects with users.
Use Attribution Models:
Utilize tools such as Google Analytics 4 to assign revenue or conversions to particular SEO activity.
Evaluate Brand Visibility:
Measure improvements in brand awareness through increased impressions and branded keyword searches.
Prioritize SEO Efforts Based on Business Needs
Identify High-Impact Areas:
Prioritize optimizing pages or keywords that have a direct impact on business goals (e.g., product pages for online stores).
Prioritize technical fixes that enhance user experience and site performance.
Balance Short-Term and Long-Term Goals:
Prioritize low-hanging fruit such as quick technical fixes or poorly performing pages for short-term gains.
Invest in long-term initiatives such as content development and link building for long-term growth.
Allocate Resources Strategically:
Utilize data-driven insight to focus on efforts that will yield the greatest ROI (such as focusing on high-conversion keywords or mobile usability).
Conclusion
The path to genuine SEO success requires optimized combinations of website functionality with content planning and website interaction quality along with third-party resource link development efforts.
Your digital success depends on a continuous approach refinement process that uses performance data to achieve business objectives in the competitive online market.
Constantly bear in mind that your target audience consists of human readers rather than machines. Write material which informs readers while entertaining them to maintain their interest as active website visitors.
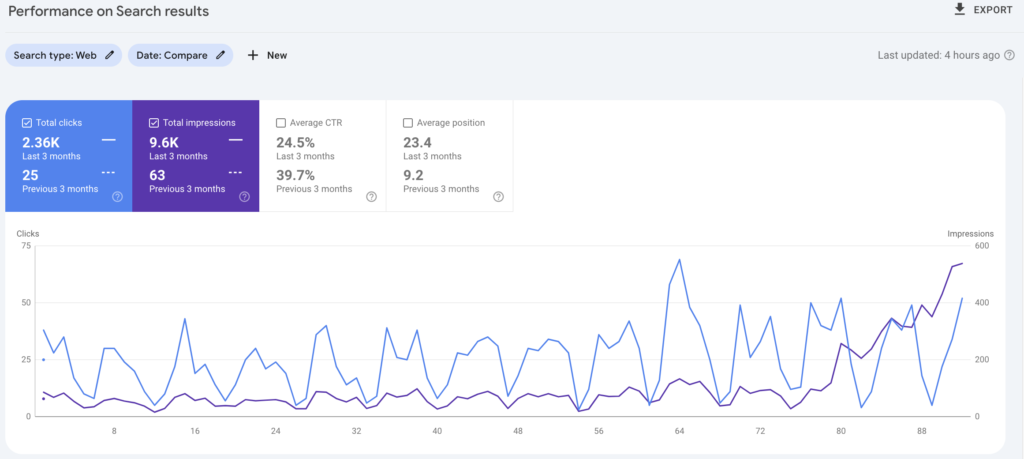
Natural distribution of those selected keywords serves as culinary spices to guide readers without overshadowing primary content. But finding the right SEO agency is important. ThriveCraft SEO has got quite the experience in this. So far, we have generated over 10 thousand leads for our clients.
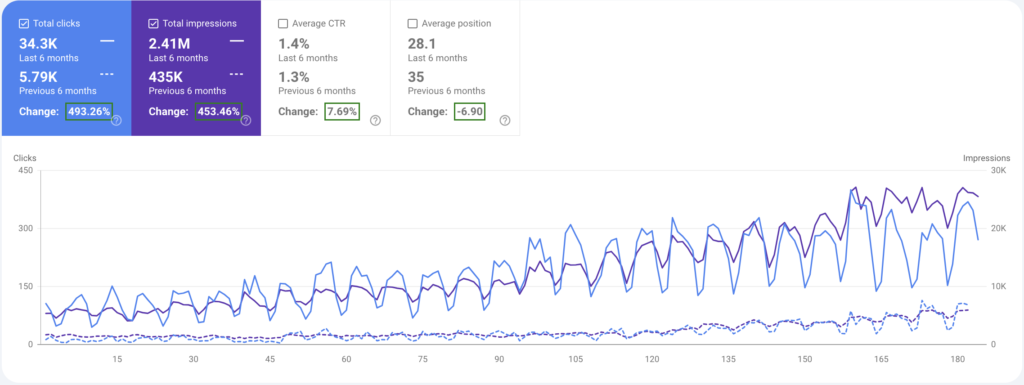
Our long-term partnership with previous clients has led to up to 1.98 million impressions. This is because of our expert-written content, organic link-building, and sustainable SEO practices. That too cost-effectively.
Ready to boost your online presence? Book your free SEO consultation.
OR
Schedule a free call to see how our SEO expertise can benefit you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
How Often Should I Update My Seo Strategy?
Businesses should modify their SEO strategies throughout a period of 3 to 6 months to follow search engine algorithm adjustments as well as user conduct patterns and industry movement patterns.
What is More Important: Content Quality or Keyword Optimization?
When it comes to content quality, it stands above all else in SEO optimization. User-provided valuable content helps establish trust with readers while building engagement along with an authority position, which indirectly enhances SEO rankings.
How do I Balance SEO and Social Media Marketing?
Optimizing social profiles, driving traffic, adapting content for social formats, and leveraging social signals for wider reach are ways to balance SEO and social media marketing.
Can I Focus Only on Organic SEO Without Paid Ads?
Yes, organic SEO, either alone or as an exclusive strategy, proves possible and efficient for sustained enhancement. To achieve search engine optimization, you must optimize your content quality, perform technical improvements, and obtain backlinks from other sites.